IVuPy
| Introduction | Examples | Download |
| Documentation |
| IVuPy Manual |
| Development Tools |
| Coin3D |
| PyQt |
| Python |
| Qt |
| ccache |
| sip |
| Indispensable Tools |
| NumPy |
| numarray |
| Numeric |
| Recommended Tools |
| Eric |
| PyQwt |
| SourceForge Host |
| Project page |
| CVS |
| Email Us |
| ivupy-users@lists.sf.net |
| © 2005-2006 |
| Gerard Vermeulen |
 |
|
|
 |
 |
Examples
surfaceviewer.py demonstrates
- how to calculate a mathematical surface in view of data transfer to Coin3D.
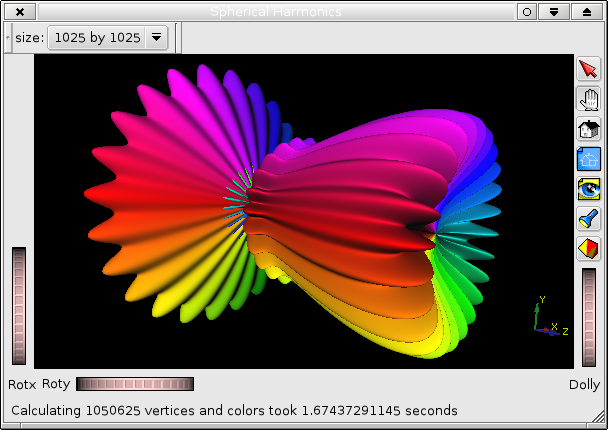
- how to color the surface to indicate the values of a scalar field. In this case the scalar field is the angle theta indicating the direction in the x-y plane.
- how to use either numpy, numarray, or Numeric. The script times a few CPU intensive operations and writes the result to the status bar, so that you can compare the speed of the different Numerical Python extensions.
- how to get an idea of the speed of Coin3D and your graphics hardware. Start with a size of 17 by 17 and set the surface in perpetual motion by a mouse stroke over the window. Increase the size step by step and watch if the movement gets jumpy. On my hardware it takes Coin3D about 6 times less time to update the view than it takes numpy to calculate a new surface.
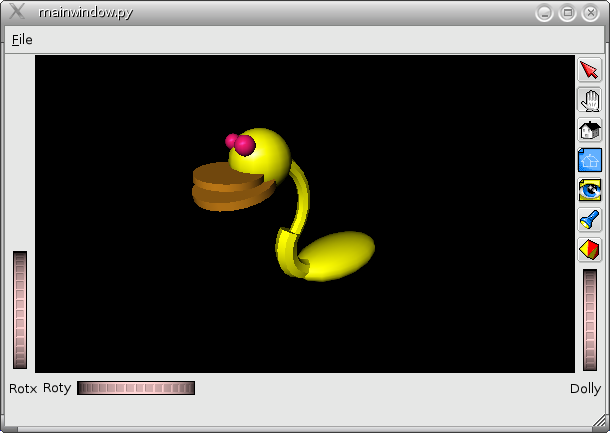
mainwindow.py demonstrates
- how to make a SoQtExaminerViewer a central widget in a subclass of QMainWindow.
- how to read Open Inventor files with PyQt and IVuPy.
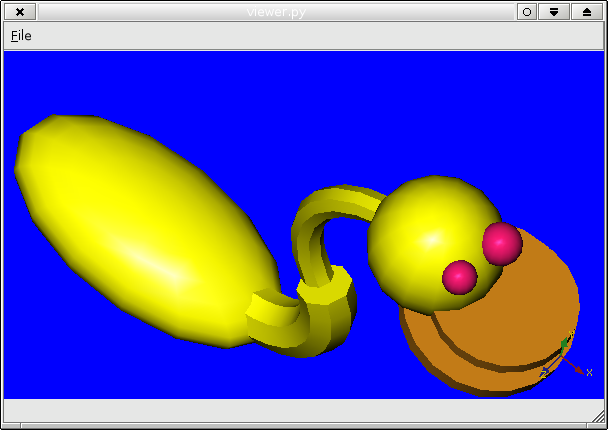
viewer.py demonstrates
- how to hide the buttons and wheels around the render area of a SoQtExaminerViewer.
- how to reimplement processSoEvent() to customize event handling.
- how to use the offscreen renderer to save a scene to a bitmap or .(e)ps file.
- how to use the PostScript vectorize action to save a scene to an .(e)ps file.
scrollview.py demonstrates
- how to embed a SoQtRenderArea in a subclass of QScrollView.
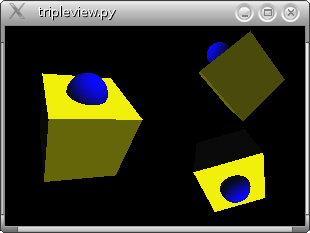
tripleview.py demonstrates
- how to put three SoQtRenderAreas with different views of the same scene graph in a QWidget.
- how to use a SoTimerSensor with a callback function to rotate the scene graph.